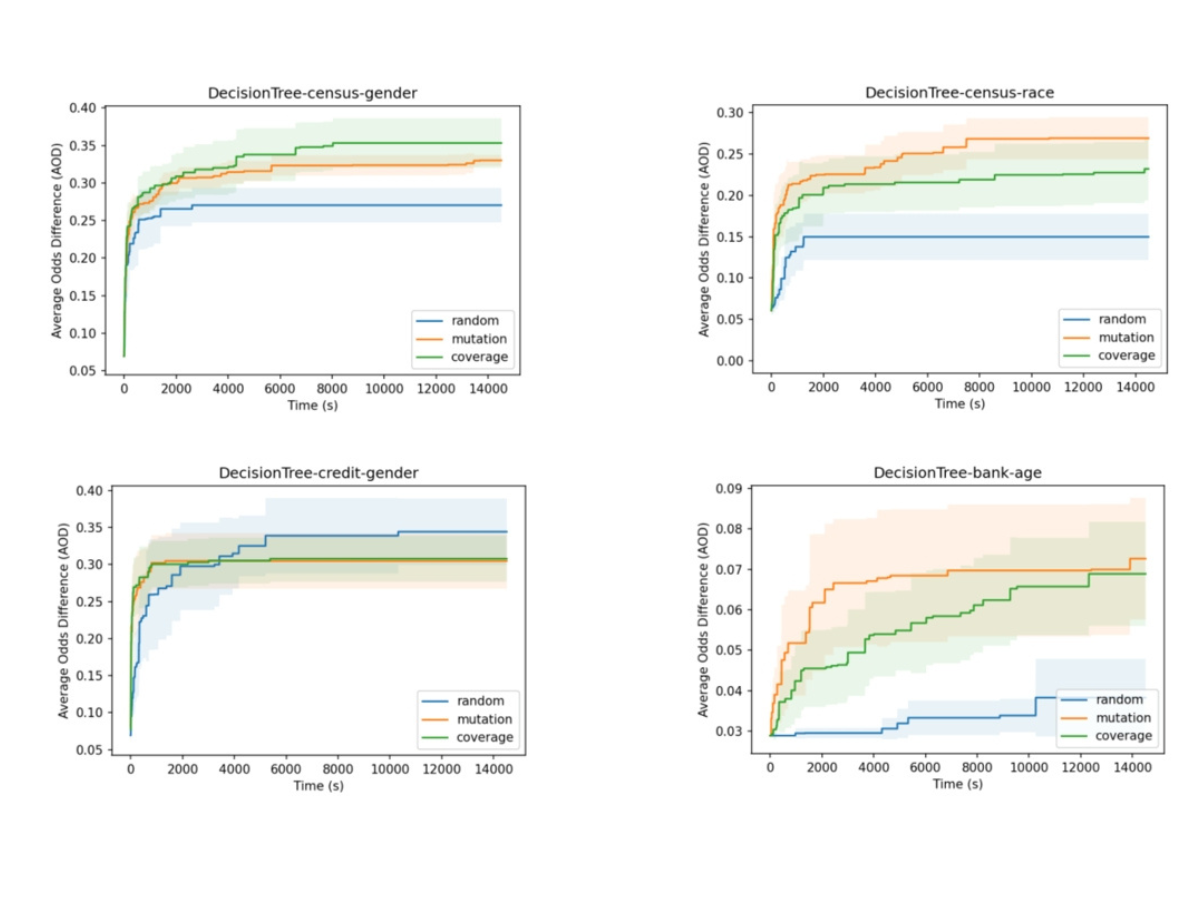
This figure shows the effectiveness of the researchers' techniques when searching for hyperparameters that can result in unfair models over time.
Tan lab focuses on making machine learning models more fair
Posted on March 11, 2025Editor’s Note: A version of this story was originally published to Penn State News.
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — G. Gary Tan, Penn State Institute for Computational and Data Sciences (ICDS) co-hire and professor of computer science and engineering, is working on a three-year, $600,000 project funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation focused on helping researchers customize fair models for their project by mitigating biases in already existing machine learning models in open-source libraries.
Computational models that appear to “think” are trained on very large datasets to learn how to identify and process information. The type of data depends on the goal of the researchers developing the model, but available datasets may raise issues of confidentiality and fairness, according to Tan. The data and how the people involved label it or feed it to the models may be biased, even unconsciously, against specific groups of people. These unbalanced datasets contain what the researchers call “fairness bias,” which could lead to unequal treatment of different groups across various demographic categories by the models.
For example, a model would be considered unfair if it predicts different outcomes for two individuals that have the same features except for a protected attribute, such as a model involved in hiring that tends to recommend more men than women, even though all other attributes are equal.
Researchers applied software testing and fuzzing, a process of generating random inputs such as demographical information to check the fairness of the models like deep neural networks and large language models. The types of inputs vary depending on the training of the model. If a model that needs users’ features to infer their income levels, inputs would include occupation, sex or race. To measure model fairness, the research team used metrics such as equal opportunity difference and average odd difference, which measure the difference of statistics between two protected groups such as how likely a job applicant is hired between a male and a female group.
The research team aims to create fairness customization recommendations for researchers.
“We want to understand what customizations within the models may produce fair or unfair models,” Tan said. “After we test and better understand what customizations can result in a fair model, we can recommend what customizations users should stay away from as they could result in an unfair model.”
Tan presented this work to the ICDS community, which encouraged him to think more broadly about the potential impact of his research.
A lot of the faculty build models from their data and are concerned about fairness. This kind of work can help them navigate the customizable space better,” Tan said.
Share
Related Posts
- Professor receives NSF grant to model cell disorder in heart
- Featured Researcher: Nick Tusay
- Multi-institutional team to use AI to evaluate social, behavioral science claims
- NSF invests in cyberinfrastructure institute to harness cosmic data
- Center for Immersive Experiences set to debut, serving researchers and students
- Distant Suns, Distant Worlds
- CyberScience Seminar: Researcher to discuss how AI can help people avoid adverse drug interactions
- AI could offer warnings about serious side effects of drug-drug interactions
- Taking RTKI drugs during radiotherapy may not aid survival, worsens side effects
- Cost-effective cloud research computing options now available for researchers
- Costs of natural disasters are increasing at the high end
- Model helps choose wind farm locations, predicts output
- Virus may jump species through ‘rock-and-roll’ motion with receptors
- Researchers seek to revolutionize catalyst design with machine learning
- Resilient Resumes team places third in Nittany AI Challenge
- ‘AI in Action’: Machine learning may help scientists explore deep sleep
- Clickbait Secrets Exposed! Humans and AI team up to improve clickbait detection
- Focusing computational power for more accurate, efficient weather forecasts
- How many Earth-like planets are around sun-like stars?
- SMH! Brains trained on e-devices may struggle to understand scientific info
- Whole genome sequencing may help officials get a handle on disease outbreaks
- New tool could reduce security analysts’ workloads by automating data triage
- Careful analysis of volcano’s plumbing system may give tips on pending eruptions
- Reducing farm greenhouse gas emissions may plant the seed for a cooler planet
- Using artificial intelligence to detect discrimination
- Four ways scholars say we can cut the chances of nasty satellite data surprises
- Game theory shows why stigmatization may not make sense in modern society
- Older adults can serve communities as engines of everyday innovation
- Pig-Pen effect: Mixing skin oil and ozone can produce a personal pollution cloud
- Researchers find genes that could help create more resilient chickens
- Despite dire predictions, levels of social support remain steady in the U.S.
- For many, friends and family, not doctors, serve as a gateway to opioid misuse
- New algorithm may help people store more pictures, share videos faster
- Head named for Ken and Mary Alice Lindquist Department of Nuclear Engineering
- Scientific evidence boosts action for activists, decreases action for scientists
- People explore options, then selectively represent good options to make difficult decisions
- Map reveals that lynching extended far beyond the deep South
- Gravitational forces in protoplanetary disks push super-Earths close to stars
- Supercomputer cluster donation helps turn high school class into climate science research lab
- Believing machines can out-do people may fuel acceptance of self-driving cars
- People more likely to trust machines than humans with their private info
- IBM donates system to Penn State to advance AI research
- ICS Seed Grants to power projects that use AI, machine learning for common good
- Penn State Berks team advances to MVP Phase of Nittany AI Challenge
- Creepy computers or people partners? Working to make AI that enhances humanity
- Sky is clearing for using AI to probe weather variability
- ‘AI will see you now’: Panel to discuss the AI revolution in health and medicine
- Privacy law scholars must address potential for nasty satellite data surprises
- Researchers take aim at hackers trying to attack high-value AI models
- Girls, economically disadvantaged less likely to get parental urging to study computers
- Seed grants awarded to projects using Twitter data
- Researchers find features that shape mechanical force during protein synthesis
- A peek at living room decor suggests how decorations vary around the world
- Interactive websites may cause antismoking messages to backfire
- Changing how government assesses risk may ease fallout from extreme financial events
- Penn State’s Leadership in AI Research
- ICS co-sponsors Health, Environment Seed Grant Program
- Symposium at U.S. Capitol seeks solutions to election security
